Hematuria is the presence of blood in a person’s urine. The two types of hematuria are
- Gross Hematuria
- Microscopic Hematuria
Hematuria is the presence of blood in a person’s urine. The two types of hematuria are
Hematuria is the presence of blood in a person’s urine. The two types of hematuria are
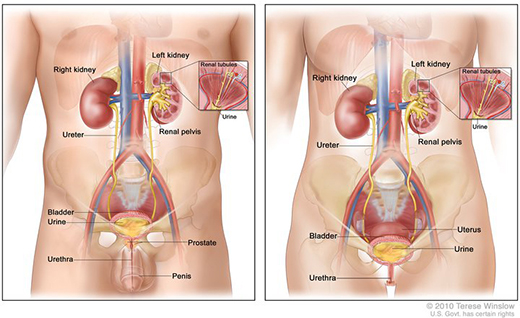
The urinary tract is the body’s drainage system for removing wastes and extra fluid. The urinary tract includes
The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs, each about the size of a fist. They are located just below the rib cage, one on each side of the spine. Every day, the kidneys filter about 120 to 150 quarts of blood to produce about 1 to 2 quarts of urine, composed of wastes and extra fluid. Children produce less urine than adults. The urine flows from the kidneys to the bladder through tubes called ureters. The bladder stores urine until releasing it through urination. When the bladder empties, urine flows out of the body through a tube called the urethra at the bottom of the bladder.
Reasons people may have blood in the urine include
More serious reasons people may have hematuria include
People who are more likely to develop hematuria may
People with gross hematuria have urine that is pink, red, or brown. Even a small amount of blood in the urine can cause urine to change color. In most cases, people with gross hematuria do not have other signs and symptoms. People with gross hematuria that includes blood clots in the urine may have bladder pain or pain in the back.
A health care professional diagnoses hematuria or the cause of the hematuria with
Taking a medical history may help a health care professional diagnose the cause of hematuria. He or she will ask the patient to provide a medical history, a review of symptoms, and a list of prescription and over-the-counter medications. The health care professional will also ask about current and past medical conditions.
During a physical exam, a health care professional most often taps on the abdomen and back, checking for pain or tenderness in the bladder and kidney area. A health care professional may perform a digital rectal exam on a man to look for any prostate problems. A health care professional may perform a pelvic exam on a woman to look for the source of possible red blood cells in the urine.
Digital rectal exam. A digital rectal exam is a physical exam of a man’s prostate and rectum. To perform the exam, the health care professional has the man bend over a table or lie on his side while holding his knees close to his chest. The health care professional slides a gloved, lubricated finger into the patient’s rectum and feels the part of the prostate that lies in front of the rectum. The digital rectal exam is used to check for prostate inflammation, an enlarged prostate, or prostate cancer.
Pelvic exam. A pelvic exam is a visual and physical exam of a woman’s pelvic organs. The health care professional has the woman lie on her back on an exam table and place her feet on the corners of the table or in supports. The health care professional looks at the pelvic organs and slides a gloved, lubricated finger into the vagina to check for problems that may be causing blood in the urine.
The health care professional can test the urine in the office using a dipstick or can send it out to a lab for analysis. Sometimes urine tests using a dipstick can be positive even though the patient has no blood in the urine, which results in a “false-positive” test. The health care professional may look for red blood cells by examining the urine under a microscope before ordering further tests.
Prior to obtaining a urine sample, the health care professional may ask a woman when she last menstruated. Sometimes blood from a woman’s menstrual period can get into her urine sample and can result in a false-positive test for hematuria. The test should be repeated after the woman stops menstruating.
Urology Cure ©2019 All rights Reserved.