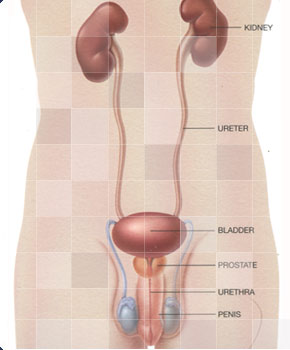
Urology is the branch of medicine that focuses on the study, diagnosis, and treatment of diseases of the urinary tract and genital organs of both males and females.
Menu
Some Reasons You May Need a Urologist
The branch of medicine focusing on studying, diagnosing, and treating diseases of the urinary tract and genital organs is known as urology. You may have been referred to a urologist if your doctor believes that you may require some type of treatment related to conditions involving the bladder, kidneys, urethra, ureters or adrenal glands.
A urologist has all of the necessary training for treating conditions like kidney and bladder stones, urinary incontinence, male infertility, tumors and infections involving the urinary tract, prostate diseases, impotence, and urinary tract malformations.
Some specialized procedures typically performed by urologists are vasectomies, circumcision, tumor removal, prostate laser treatment, destruction of kidney stones, penile implant insertion, bladder suspension, laparoscopic procedures and pelvic floor reconstructions.
Urinary Tract Symptoms
The urinary tract is a more complex area of the body than many people realize. Some symptoms that you may experience that involve the urinary tract include the following:
Kidney Pain
People typically experience kidney pain as a dull, constant ache in their back just under their ribs and near the spine. This type of pain will typically spread to the area under the ribs toward the bellybutton area.
Kidney infections normally involve rapid swelling and ureter obstruction. You should realize, however, that a number of kidney diseases do not cause pain and progress very slowly. Such diseases include cancer, polycystic kidney, and stagorn calculus.
Ureteral Pain
The ureter is the part of the body that is a duct that allows urine to travel from your kidneys to your bladder. When you experience ureter pain, it is normally due to some type of obstruction, such as a blood clot or a stone passing. The type of pain that this produces is due to ureter spasms because it is attempting to rid itself of the obstruction or foreign body.
Your doctor or urologist may be able to determine a ureteral stone location by the site of referral and your description of the pain. In cases where a stone is located in the upper part of the ureter, you will likely be experiencing pain radiating into the testicle. If the stone or stones is located in the middle of your ureter, you may be experiencing pain in the right lower quadrant of your abdomen. In the case of a mild obstruction, there is normally no pain in the ureter or kidney.
Bladder Pain
Bladder pain is sometimes due to a urinary tract infection. If you are experiencing urination that is painful, burning, and frequent, that does not resolve with antibiotics, it could indicate a condition called interstitial cystitis. Your urologist will perform a urine test and use a special instrument to examine your bladder in making their diagnosis. This condition is typically treated using anti-inflammatory drugs. You may be able to prevent it by avoiding known triggers, including alcohol, caffeine, spicy foods and chocolate.
Prostate Pain
Pain from the prostate itself is uncommon, but could indicate a condition called acute bacterial prostatitis. Men of any age can develop the condition, which begins suddenly with severe prostate symptoms. It is vital to seek treatment immediately.
Urination tends to be difficult and very painful. Other symptoms include lower back pain, fever, chills, frequent urination, or urinary urgency, particularly at night. You may also have bodily aches and pains.
Testicular Pain
Testicular pain can be very severe when it is caused by infection, trauma, or a twisted spermatic cord. It is usually experienced locally, although it can radiate into the lower abdomen.
Hernia
A hernia can develop whenever tissue begins pushing through weak abdominal muscles. Inguinal hernias are a type that moves into the scrotum, leading to swelling and testicular pain.
Your doctor or urologist may be able to minimize an inguinal hernia or put it back into its place. When this fails, hernias can be corrected surgically.
Kidney Stones
In some cases, kidney stones create pain that spreads into the testicles. This is known as referred pain, where the pain is experienced beyond the actual source of the pain.
Other kidney stone symptoms include:
- Blood-colored urine
- Painful urination or burning during urination
- Nausea
- Pain at the head of the penis
- Acute pain radiating from the back to the groin area
- Frequent urination
- Vomiting
If you have a kidney stone, your doctor or urologist may recommend that you wait for it to pass. But in cases where it has not passed for a long period of time, or you experience signs of an infection, you should seek immediate care.
Besides surgical treatment, kidney stones can be treated using ultrasound to break up the stones.
Urination Symptoms
There are quite a few conditions that can cause symptoms related to urination, including bladder infections, prostatitis, bladder inflammation, or the presence of foreign bodies within the bladder. In many cases, a patient with chronic cystitis will not have any symptoms.
Bladder Outlet Obstruction Symptoms
Being hesitant in starting a urinary flow is one early indication of bladder obstruction. As the obstruction increases, this hesitancy tends to grow longer, and the patient may be straining to pass urine past this obstruction. Obstruction of the prostate and urethra narrowing are common symptoms.
Hesitating
One early symptom of bladder obstruction is hesitancy in starting a urinary stream. After the obstruction progresses, hesitancy lasts longer, and the patient may find themselves straining to force the flow of urine through this obstruction. Common causes of the symptoms are narrowing of the urethra and prostate obstruction.
Urgency
Having a sudden, strong desire to urinate can be due to bladder irritability and hyperactivity that is caused by inflammation, an obstruction, or a neurological bladder disease. Typically, the patient can temporarily control their sudden need to urinate, but a small flow of urine may still occur.
Acute Urinary Retention
If you suddenly are unable to urinate, this is known as acute urinary retention. If you experience this, it will definitely be noticeable, as you will experience severe pain right above your pubic bone, and small amounts of urine may dribble out.
Chronic Urinary Retention
You’ll probably experience minimal discomfort if you experience chronic urinary retention. The flow of your urine may be reduced, and you may be hesitant in initiating the stream. Urine may constantly dribble when you have this condition.
Urinary Stream Interruption
The interruption of your urine stream may be abrupt and lead to severe pain that radiates down through the urethra. In most cases, you will be dealing with bladder stones if you experience this type of reaction.
Residual Urine Sense
You may feel that your bladder has retained urine, even after you have completed urinating.
Incontinence
If you are experiencing incontinence, it can be due to a variety of reasons.
True Incontinence
You may abruptly lose urine, which may be continual or periodic. This is most often caused by fistulas and congenital defects. A urethra sphincter injury can happen during childbirth or resection of the prostate.
Stress-Induced Incontinence
If the sphincter is somewhat weak, you may lose urine because you are physically straining, such as laughing, coughing, or getting up from a chair. This is more common among women who tend to have weaker muscle support because of multiple births.
Urge Incontinence
The need to urinate may be so strong that loss of urine occurs involuntarily. This is also a common symptom related to a motor neuron lesion.
Overflow Incontinence
This occurs due to a flaccid bladder or chronic urinary retention.
Urine in Blood
Blood found in the urine is a symptom that cannot be ignored. A few conditions that can cause it are kidney stones, bladder tumors or infections. It is important to note if the urination is painful or not, for proper diagnosis.
Sexual Problems
It is common for those undergoing emotional or psychological problems to have associated urinary complaints. Or those with existing symptoms may see them exacerbated due to tension.
If you are a woman, menstruation must be taken into account, since it can increase both functional and organic bladder and kidney problems.
Men may experience sexual difficulties related to urinary problems, but they tend to be bashful about discussing any loss of sexual potency. Among men, sexual symptoms include premature erection loss, impaired erection quality, premature ejaculation, and loss of libido. Men are encouraged to openly discuss the symptoms with their physician so that they receive needed care.
Female Sexual Difficulties
Women normally experience an unhappy sex life when they have psychosomatic cystitis syndrome. If you have this condition, you will likely notice an increased frequency of urination, or pain following the sexual act in the form of vaginal or urethra pain.
NEED ASSISTANCE?
Reach us now!
[contact-form-7 id="2885"]
Sign up to get the latest news and deals on Urology treatments!
get social:
Urology Cure ©2019 All rights Reserved.
